
The world’s e-waste problem is reaching staggering new heights, with global electronic waste surging 82% since 2010, and an estimated 62 million tonnes generated in 2022 alone.
That’s enough to fill 1.55 million 40-tonne trucks, forming a bumper-to-bumper line around the equator. As the UN’s fourth Global E-waste Monitor (GEM) warns, this trend shows no signs of slowing, with projections of e-waste hitting 82 million tonnes by 2030—an alarming 33% increase.
The findings, released today by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and UNITAR, shine a light on the significant financial and environmental losses tied to mismanaged e-waste. In 2022, less than 23% of all electronic waste was properly collected and recycled, leaving a staggering $62 billion in valuable resources untapped and at risk of polluting communities worldwide.
Are Billions in Resources Being Squandered Due to E-Waste Opportunities?
Among the hidden costs of improper e-waste disposal lies the loss of critical resources. Only 1% of global demand for rare earth elements—crucial to the technologies driving our digital and sustainable future—was met through recycling in 2022. These resources, including essential metals like copper, gold, and iron, could play a pivotal role in building the renewable energy infrastructure of tomorrow. Instead, they are being squandered, dumped in landfills, or lost to illegal shipments, costing us not just financially but environmentally.
According to the GEM report, formal recycling efforts currently lag five times behind the pace at which e-waste is generated. To put that into perspective, in 2022 alone, the embedded metals in e-waste were valued at an astounding $91 billion. Yet, only $28 billion of these resources were reclaimed through proper recycling.
Health Hazards and Environmental Dangers Looming Due to E-Waste Mismanagement
Beyond the missed financial opportunities, e-waste poses severe health and environmental hazards. The toxic substances found in discarded electronics, including mercury, lead, and cadmium, can wreak havoc on ecosystems and human health. Mercury, in particular, is a notorious neurotoxin that can impair brain development and damage the nervous system, making it imperative to tackle this issue head-on.
Experts like Nikhil Seth, Executive Director of UNITAR, are calling for urgent attention “Amidst the hopeful embrace of solar panels and electronic equipment to combat the climate crisis and drive digital progress, the surge in e-waste requires urgent attention.”
While the world races towards renewable energy and digital progress, the mounting e-waste crisis threatens to undermine our efforts.
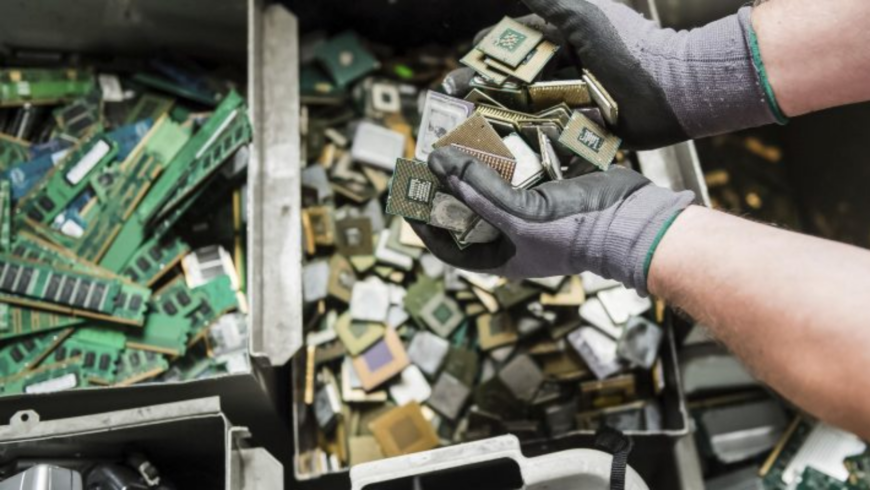

Can We Forge a Path to Positive Change Through Better E-Waste Management?
“Many in today’s society use multiple computers and phones, an ever-growing number of new appliances, monitors and sensors, e-bikes, e-scooters, clothes, toys, and furniture with embedded electronics, electric tools, and energy-saving equipment such as LEDs, photovoltaics, and heat pumps. Urban and remote areas are increasingly connected to the Internet, and a growing number of data centers cater to the needs of the digital transformation. In the face of all this, concrete steps are urgently needed to address and reduce e-waste. Improved e-waste management could result in a global net positive of USD 38 billion, representing a significant economic opportunity while addressing climate change and health impacts.” Said Ruediger Kuehr, Senior Manager, Sustainable Cycles (SCYCLE) Programme, UNITAR / Adjunct Professor, University of Limerick (Ireland).
If global e-waste collection and recycling rates were increased to 60% by 2030, the potential economic benefits would exceed $38 billion. Not only would this minimize environmental and health risks, but it would also lead to significant savings by reducing the need for raw materials extraction.
Moreover, E-waste can be a source of income for individuals or industries. For example, in Bangalore (India), around 18,000 MT of e-wastes is generated annually. These e-wastes do have some precious metals like gold, silver, platinum, copper, aluminum, and rare earth metals and these elements can be reused. Furthermore, new commercial benefits from them can also be explored as opportunities.(National Center for Biotechnology information, 2023).
The solutions are clear, greater investment in recycling infrastructure, a stronger focus on repair and reuse, and stricter regulations to curb illegal e-waste shipments. We have the opportunity to turn the e-waste crisis into a global opportunity—if we act now.
E-Waste by the Numbers
- 62 million tonnes: E-waste generated in 2022, equivalent to the weight of 107,000 of the world’s largest passenger aircraft.
- $91 billion: Value of metals embedded in e-waste, including $19 billion in copper, $15 billion in gold, and $16 billion in iron.
- 22.3%: Proportion of e-waste properly recycled in 2022.
- 5.1 million tones: E-waste shipped across borders in 2022, of which 65% went from high-income to middle- and low-income countries.
As Vanessa Gray, Head of ITU’s Environment and Emergency Telecommunications Division, points out, “The Global E-waste Monitor shows that we are currently wasting USD 91 billion in valuable metals due to insufficient e-waste recycling. We must seize the economic and environmental benefits of proper e-waste management; otherwise, the digital ambitions of our future generations will face significant risks.”
The benefits of proper e-waste management are clear, both for the environment and the economy. If we don’t act now, the consequences will be felt by future generations.
How You Can Help the Environment and Reduce E-Waste with Asia Data Destruction Services
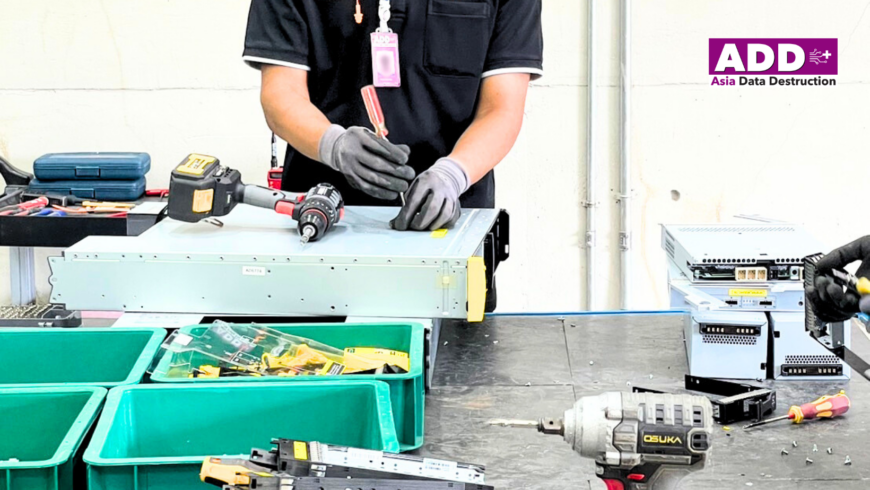

We are committed to addressing the e-waste crisis through comprehensive and responsible IT asset disposal services.
Here’s how our services can help you contribute to a more sustainable future
- Secure Data Destruction: We ensure that all data on your old electronic devices is securely erased, protecting sensitive information from falling into the wrong hands.
- Responsible Recycling: We follow stringent environmental guidelines to ensure that e-waste is processed in a way that minimizes pollution and maximizes resource recovery.
- Extending Device Life: Through refurbishment and reuse programs, we help extend the life of electronics, reducing the need for new devices and the associated environmental impact.
- Carbon Footprint Reduction Report: After using our services, we provide you with a detailed carbon footprint reduction report. This helps you quantify the environmental benefits of responsible e-waste disposal and demonstrates your commitment to sustainability.
- Regulatory Compliance: Our services comply with international standards, ensuring that your e-waste disposal meets all legal requirements and contributes to global recycling efforts.
By choosing ADD, you are not only ensuring the secure disposal of your IT assets but also helping to close the gap in e-waste recycling and reduce the environmental impact of electronic waste.
Join us in making a difference. Contact Asia Data Destruction today to learn more about how we can assist with your e-waste management needs.
Source:
- https://www.itu.int/en/mediacentre/Pages/PR-2024-03-20-e-waste-recycling.aspx
- https://unitar.org/about/news-stories/press/global-e-waste-monitor-2024-electronic-waste-rising-five-times-faster-documented-e-waste-recycling
- Concepts of circular economy for sustainable management of electronic wastes: challenges and management options – PMC (nih.gov)

 ไทย
ไทย 日本語
日本語 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt ភាសាខ្មែរ
ភាសាខ្មែរ


